Floods are among the most devastating natural disasters that can affect homeowners, yet many people do not fully understand the importance of flood insurance or even realize that their standard home insurance policies do not cover flood damage. While home insurance protects your property from various disasters, such as fire, theft, and vandalism, flooding is typically excluded. This is where flood insurance comes in, offering essential protection for homeowners in flood-prone areas.
In this article, we will explore the role of flood insurance in homeowners’ coverage, how it works, and why it is crucial for homeowners, especially those living in high-risk areas.
What is Flood Insurance?
Flood insurance is a type of property insurance specifically designed to cover damage to your home, belongings, and other structures caused by flooding. Unlike a standard homeowners insurance policy, which often excludes flood-related damages, flood insurance provides coverage for losses incurred from a flood, including rising water, heavy rain, or water overflowing from rivers, lakes, or other bodies of water.
Flood insurance is typically offered through the National Flood Insurance Program (NFIP), which is managed by the Federal Emergency Management Agency (FEMA). In addition to the NFIP, some private insurance companies also offer flood insurance policies.
Why is Flood Insurance Important?
Many homeowners may assume that their home insurance will cover flood damage, but most policies exclude this type of event. Unfortunately, flooding can cause severe damage, ranging from structural issues to the destruction of personal belongings, and without proper coverage, homeowners are left to foot the bill for repairs, which can be costly.
In the United States, floods are the most common and expensive natural disaster. According to FEMA, just one inch of floodwater in a home can cause more than $25,000 worth of damage. As a result, homeowners living in flood-prone areas or in regions that are vulnerable to hurricanes, heavy rains, or rapid snowmelt may be at higher risk of flooding and should consider obtaining flood insurance.
How Does Flood Insurance Work?
Flood insurance typically consists of two separate policies:
- Building Property Coverage: This portion of the policy covers damage to the structure of your home, including the foundation, walls, roof, and other permanent features like built-in appliances and plumbing systems. It also covers damage to detached structures on your property, such as a garage or shed.
- Personal Property Coverage: This part covers damage to personal belongings, such as furniture, clothing, electronics, and appliances. It also covers items stored in basements or lower levels, which are especially vulnerable to flood damage.
Flood insurance policies may have different coverage limits depending on the insurer and the specific policy. The NFIP, for instance, offers coverage limits of up to $250,000 for the structure of your home and up to $100,000 for personal property. If you own a high-value home or have expensive belongings, you may need to purchase additional coverage to ensure you are fully protected.
Who Needs Flood Insurance?
Flood insurance is not required by law in most areas, but if you live in a high-risk flood zone, it may be required by your mortgage lender. FEMA designates flood-prone areas as Special Flood Hazard Areas (SFHAs), which are mapped on flood maps known as Flood Insurance Rate Maps (FIRMs). If your home is located in an SFHA, you are more likely to experience flooding and may be required to carry flood insurance as a condition of your mortgage.
However, even if you live outside of an SFHA, flood insurance can still be valuable. It’s important to note that floods can occur in areas that are not typically prone to flooding. Heavy rainfall, changes in land development, and other environmental factors can increase flood risks in areas that were previously considered safe.
What Does Flood Insurance Cover?
Flood insurance typically covers the following:
- Damage to the structure of the home, including foundations, walls, and flooring, from rising floodwaters.
- Personal property, such as furniture, clothing, electronics, and appliances that are damaged by flooding.
- Damage to other structures, such as a garage or tool shed, located on the property.
In addition to these basics, flood insurance may also cover:
- Basement damage: While most standard homeowners insurance policies exclude basement coverage, flood insurance may cover damages to finished basements and personal items stored there, such as furniture or electronics. However, the NFIP limits basement coverage for certain items, such as carpeting, furniture, and personal items.
- Cleanup costs: Flood insurance may cover some of the costs of cleaning up after a flood, including debris removal, if specified in the policy.
- Temporary living expenses: Some policies offer additional coverage for temporary living expenses if you are unable to stay in your home while repairs are made after a flood.
What is Not Covered by Flood Insurance?
While flood insurance provides valuable protection, there are certain exclusions. Common exclusions include:
- Losses due to lack of maintenance: Flood insurance will not cover damage caused by poor maintenance, such as clogged gutters or failing to repair a roof leak.
- Earthquakes, landslides, and mudslides: Flood insurance does not cover damage caused by events like earthquakes or mudslides, even if they occur as a result of flooding.
- Sewer backups: Flood insurance does not cover damage from sewer backups, unless the backup is directly caused by rising floodwaters.
- Certain types of personal property: Some personal property, such as currency, valuable papers, and items stored in the basement, may be excluded from coverage or limited.
If you need coverage for these types of events or damages, you may need to look into separate insurance policies, such as earthquake insurance or sewer backup insurance.
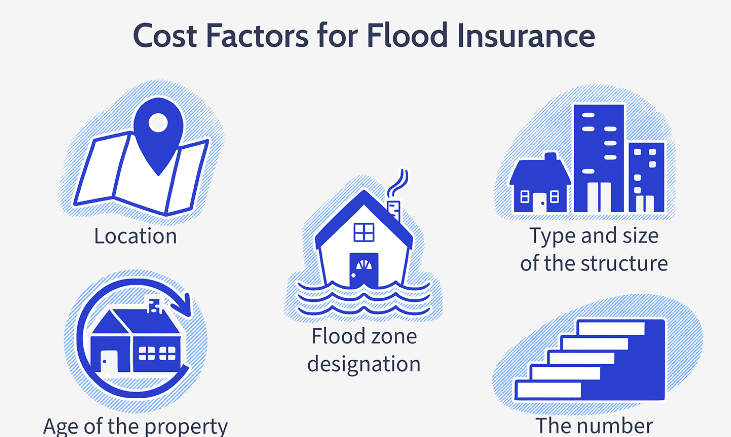
How Much Does Flood Insurance Cost?
The cost of flood insurance varies depending on factors such as:
- Location: Homes in high-risk flood zones (SFHAs) will typically have higher premiums than homes in low- or moderate-risk areas.
- Coverage amount: The more coverage you need, the higher the premium. This includes the structure of your home, personal property, and additional coverage for detached structures.
- Building characteristics: The age, construction type, and elevation of your home can affect your flood insurance rates. Homes built at a higher elevation are generally less likely to flood and may have lower premiums.
- Deductible: Like other types of insurance, flood insurance policies come with deductibles. A higher deductible will typically result in lower premiums, but you’ll pay more out of pocket in the event of a claim.
For properties in moderate- to low-risk areas, flood insurance can be surprisingly affordable, often costing just a few hundred dollars a year. However, homes in high-risk areas can face much higher premiums, particularly if they are located in areas prone to frequent or severe flooding.
When Should You Buy Flood Insurance?
Flood insurance typically takes 30 days to go into effect after you purchase the policy, so it’s important to plan ahead. Ideally, homeowners should purchase flood insurance well before they are at risk of experiencing a flood. In addition, it’s crucial to review and update your flood insurance coverage periodically, especially if you make significant changes to your home or property.
If you live in a flood-prone area, having flood insurance in place can be the difference between financial hardship and recovery after a disaster. Even if you don’t live in a high-risk area, consider purchasing flood insurance to ensure you are protected from unexpected flooding.
Conclusion
Floods can cause devastating damage to homes and personal property, making flood insurance an essential component of homeowners’ coverage. While home insurance policies typically exclude flood damage, purchasing a separate flood insurance policy through the NFIP or a private insurer can help safeguard your property and belongings.
Before buying flood insurance, it’s important to assess your flood risk, understand the coverage options, and review policy exclusions. While it may not be a requirement for all homeowners, flood insurance offers invaluable protection and can provide peace of mind when natural disasters strike. With the right coverage in place, you can ensure that your home is protected against one of the most unpredictable and destructive forces of nature.
Leave a Reply